Background of CHOK1-ADCC+ cell line system
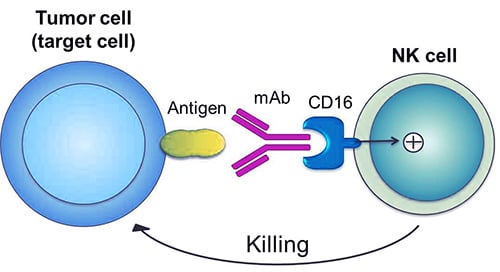
The typical ADCC involves activation of NK cells by antibodies in a multi-tiered progression of immune control. Once the Fc receptor of NK cell binds to the Fc region of the antibody, the NK cell releases cytotoxic factors that cause the death of the target cell.
The binding ability of the Fc and FcγRIIIa affects the ADCC activity. Therefore, by enhancing the affinity of the antibody to CD16a, the ADCC activity is enhanced, and the clinical therapeutic effect of the antibody is enhanced.
ProBio scientists strategically knocked out a gene in CHOK1 cells that is responsible for the fucose bind to N-glycans in order to produce afucosylated antibodies.
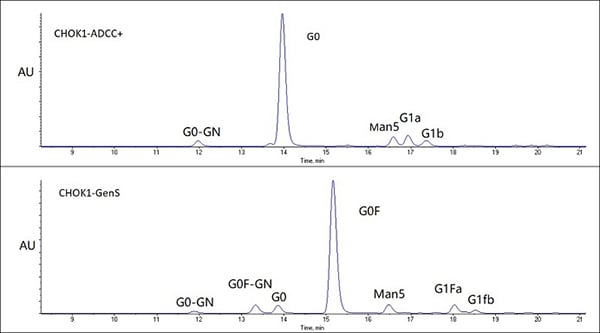
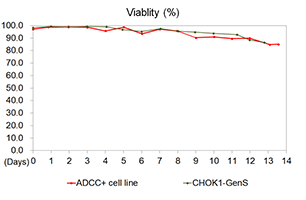
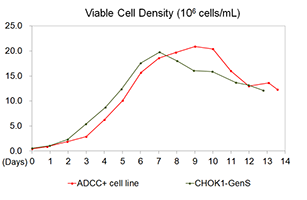
The antibody produced by modified cell line CHOK1-ADCC+ is successfully afucosylated. CHOK1-ADCC+has a similar performance in antibody expression and growth compared to wild type CHOK1-GenS.
-
Glycan Profiling
-
Cell Growth Performance
Features of CHOK1-ADCC+ cell line system

ADCC activity enhanced
- Enhance affinity to FcγIIIa
- Enhance ADCC activity
-
Service
- Proprietary CHOK1-ADCC+ cell line system to produce afucosylated antibodies
- Transient Expression/Cell pool/Cell line for different customers in late discovery stage or in CMC stage

Host cell System
- 2 CHO-K1 host cell license to choose :
wild-type CHOK1-GenS
ADCC enhanced CHOK1-ADCC+ - Purchase in combination with wild type CHOK1-GenS cell line, and get a discounted price.
- Royalty-free
- Direct sublicense from ProBio
- 2 CHO-K1 host cell license to choose :
-
CD16a 158V/F affinity (BLI)
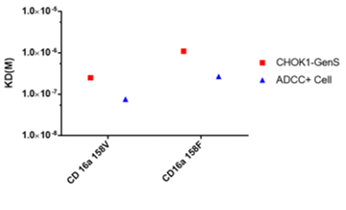
- The affinity to CD16a (158V and 158F) was increased by 3-4 times.
-
PBMC-based ADCC
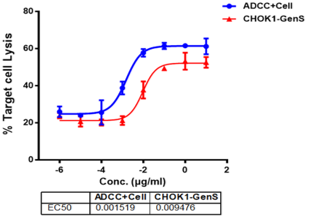
- Cytotoxicity is increased by about 10%.
- Effect concentration (EC50) was reduced by 6 times.
- ADCC effect was significantly enhanced.
| Service Package | Antibody Transient Expression | Cell pool development & developability assessment | Cell line development PCB & PCB stability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Timeline | 8.5 weeks | 12 weeks (mAb, protein) 14 weeks (bsAb) |
16 weeks (mAb, protein) 18 weeks (bsAb) |
| Delivery | ROA | 4 Mix pools | 6 PCBs |
| Application scenario | Late discovery stage, after get human or humanized antibody candidates | Late discovery stage, after get human or humanized antibody candidates | Preclinical CMC development |
| Benefits to clients |
|
|
|
Reference:
1.Hashimoto, G.; Wright, P. F.; Karzon, D. T. (1983-11-01). "Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity against influenza virus-infected cells". The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 148 (5): 785–794.
2.Lo Nigro, Cristiana; Macagno, Marco; Sangiolo, Dario; Bertolaccini, Luca; Aglietta, Massimo; Merlano, Marco Carlo (March 2019). "NK-mediated antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in solid tumors: biological evidence and clinical perspectives". Annals of Translational Medicine. 7 (5): 105.

